Embedded Multicore Building Blocks (EMB²)
=========================================
Introduction
------------
### Overview
The Embedded Multicore Building Blocks (EMB²) are an easy to use yet powerful and efficient C/C++ library for the development of parallel applications. EMB² has been specifically designed for embedded systems and the typical requirements that accompany them, such as real-time capability and constraints on memory consumption. As a major advantage, low-level operations are hidden in the library which relieves software developers from the burden of thread management and synchronization. This not only improves productivity of parallel software development, but also results in increased reliability and performance of the applications.
EMB² is independent of the hardware architecture (x86, ARM, ...) and runs on various platforms, from small devices to large systems containing numerous processor cores. It builds on MTAPI, a standardized programming interface for leveraging task parallelism in embedded systems containing symmetric or asymmetric (heterogeneous) multicore processors. A core feature of MTAPI is low-overhead scheduling of fine-grained tasks among the available cores during runtime. Unlike existing libraries, EMB² supports task priorities and affinities, which allows the creation of soft real-time systems. Additionally, the scheduling strategy can be optimized for non-functional requirements such as minimal latency and fairness.
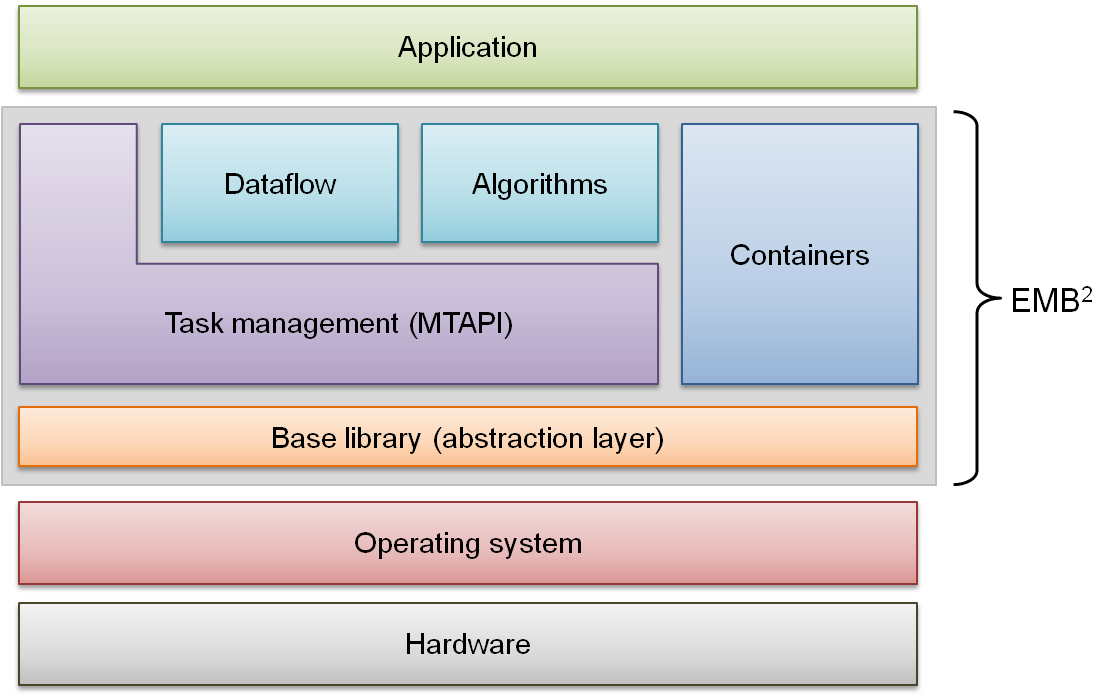
Besides the task scheduler, EMB² provides basic parallel algorithms, concurrent data structures, and skeletons for implementing stream processing applications (see figure below). These building blocks are largely implemented in a non-blocking fashion, thus preventing frequently encountered pitfalls like lock contention, deadlocks, and priority inversion. As another advantage in real-time systems, the algorithms and data structures give certain progress guarantees. For example, wait-free data structures guarantee system-wide progress which means that every operation completes within a finite number of steps independently of any other concurrent operations on the same data structure.
 ### Community and Contact
GitHub:
- https://github.com/siemens/embb
Repository:
- https://github.com/siemens/embb.git (HTTP)
- git@github.com:siemens/embb.git (SSH)
Mailing lists:
- embb-announcements@googlegroups.com (announcements)
### Community and Contact
GitHub:
- https://github.com/siemens/embb
Repository:
- https://github.com/siemens/embb.git (HTTP)
- git@github.com:siemens/embb.git (SSH)
Mailing lists:
- embb-announcements@googlegroups.com (announcements)
https://groups.google.com/forum/#!forum/embb-announcements/join
- embb-dev@googlegroups.com (development)
https://groups.google.com/forum/#!forum/embb-dev/join
Contact:
- embb.info@gmail.com
### License
See the file [COPYING.md](https://github.com/siemens/embb/blob/master/COPYING.md) in the project's root directory.
### Contributions
See the file [CONTRIBUTING.md](https://github.com/siemens/embb/blob/master/CONTRIBUTING.md) in the project's root directory.
Build and Installation
----------------------
### General
It is strongly recommended to build from a release file and not from a repository snapshot in order to get the documentation and the examples out-of-the box. The release files can be found at https://github.com/siemens/embb/releases.
### Platforms
EMB² is regularly built and tested on a variety of OS/compiler/architecture combinations including Linux (x86 and ARM using GCC/Clang) and Windows (x86 using MSVC). Other platforms may be supported without any changes to the source code. The project comes with unit tests that can be used to find out whether a system not officially supported is suitable to run EMB². If the build process or the unit tests fail on your system, please contact us.
### Prerequisites
The project is based on the standards C99 (for C code) and C++03 (for C++ code) to be usable on a wide range of target systems. Besides a C/C++ compiler supporting these standards, you need CMake 2.8.9 or higher. [CMake](https://cmake.org/) is a build file generator which abstracts from the concrete build tools.
### Quick Installation on Linux
To generate and invoke the platform-specific build files, open a shell and change to the project's root directory. Create a subdirectory, where you want to build the library, e.g., "build", and change to that subdirectory. In the following, it is assumed that the project's root directory is the parent directory. Now you can generate the build files using CMake:
cmake ..
As the next step, compile EMB² using the generated build files:
cmake --build .
After compilation has finished, execute the tests:
binaries/run_tests.sh
Finally, install EMB² (the default path is `/usr/local`):
sudo cmake --build . --target install
### Quick Installation on Windows
To generate and invoke the platform-specific build files, open a Visual Studio developer shell and change to the project's root directory. Create a subdirectory, where you want to build the library, e.g., "build", and change to that subdirectory. In the following, it is assumed that the project's root directory is the parent directory. Now you can generate the build files using CMake (a list of supported CMake generators can be displayed by typing `cmake --help`). For example:
cmake -G "Visual Studio 14 2015" ..
As the next step, compile EMB² using the generated build files:
cmake --build . --config Release
After compilation has finished, execute the tests:
binaries\run_tests.bat
Finally, install EMB² with *administrator privileges*:
cmake --build . --target install --config Release
### Detailed Installation Instructions
EMB² provides several options which allow you to configure it to your needs. This section explains these options and describes the build process in more detail.
#### 1. Generation of Native Build Files
As mentioned above, it is recommended to build EMB² in a subdirectory, e.g., "build". The actual build files are generated by the following command (a list of available generators can be displayed by typing `cmake --help`):
cmake -G .. [OPTIONS]
Note that on Linux, the architecture (32/64 bit) cannot be selected by the generator. The default is "Unix Makefiles" for which reason `-G ` may be omitted.
EMB² can be built in Release or Debug mode. The latter contains additional checks during runtime and is only recommended for development purposes. On Linux, the build mode can be specified using the option `-DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=[Release|Debug]`, for example:
cmake .. -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=Debug
If no build mode is given, the default (Release) is used. The Visual Studio generators create build files for both modes (the selection is done at build time).
You may choose a custom compiler instead the default one by defining `CMAKE_CXX_COMPILER` and/or `CMAKE_C_COMPILER`. For example, to use Clang on Linux, type:
cmake .. -DCMAKE_CXX_COMPILER=clang++ -DCMAKE_C_COMPILER=clang
In the same way, you may cross compile to another platform. For example, to cross compile to ARM v7 using GCC, you need to specify the cross compiler itself and the target architecture as an argument to the compiler:
cmake .. -DCMAKE_CXX_COMPILER=arm-linux-gnueabi-gcc++ \
-DCMAKE_CXX_FLAGS=-march=armv7-a \
-DCMAKE_C_COMPILER=arm-linux-gnueabi-gcc \
-DCMAKE_C_FLAGS=-march=armv7-a
EMB² can be built with C++ exception handling (default) or without exceptions. When exceptions are turned off, a message is emitted in case of an error and the program aborts. To disable exceptions, add the option `-DUSE_EXCEPTIONS=OFF`.
Similarly, automatic initialization of the task scheduler by the MTAPI C++ interface can be disabled with `-DUSE_AUTOMATIC_INITIALIZATION=OFF`. This way, unexpected delays after startup can be avoided, e.g. for timing measurements.
The tutorial of EMB² comes with a number of examples in `doc/examples/`. These can be built with the other source files using the option `-DBUILD_EXAMPLES=ON`. Note, however, that the examples use C++11 features and require a recent compiler.
By default, the included unit tests are built as part of the installation process. To override the default behavior, add the option `-DBUILD_TESTS=OFF`.
#### 2. Compiling and Linking
As the next step, you can compile the library using the generated build files. On Linux, the build mode (Release|Debug) is already given in the build files, whereas on Windows, it has to be specified now.
For a Linux build, type
cmake --build .
For a Windows Release build, type
cmake --build . --config Release
#### 3. Running the Tests
To check whether EMB² was compiled correctly, run the tests. The test executables are contained in the subfolder "binaries".
On Linux, type
binaries/run_tests.sh
On Windows, type
binaries\run_tests.bat
If no error message occurs, EMB² works fine.
#### 4. Installation
The default installation path on Linux is
/usr/local/
and on Windows
C:\Program Files\embb-X.Y.Z\
or
C:\Program Files (x86)\embb-X.Y.Z
depending on the target architecture.
If you want a different installation path, you can change it now by typing
cmake -DINSTALL_PREFIX=YourCustomPath ..
To install the files, use the command
cmake --build . --target install
which copies the contents of the "install" folder to the "bin", "lib", and
"include" folders in the installation path. For the default paths, the
installation has to be run with administrator / root privileges.
Using the Library
-----------------
To use EMB², the include files have to be made available during compilation of
your application and the libraries have to be added during linking.
### 1. Using C++
If you want to use the C++ functionalities of EMB², you have to link the
following libraries (names will be different on Windows and on Linux) in the
given order:
embb_dataflow_cpp, embb_algorithms_cpp, embb_containers_cpp,
embb_mtapi_cpp, embb_mtapi_c, embb_base_cpp, embb_base_c
The C++ header files can be included as follows:
#include
#include
#include
#include
### 2. Using C
The following libraries have to be linked in the given order:
embb_mtapi_c, embb_base_c
The C header files can be included as follows:
#include or #include
#include
Documentation
-------------
The release files of EMB² come with a tutorial, example programs, and a
reference manual (HTML) describing the APIs. All documentation is contained in
the "doc" folder. The root document of the HTML reference is
"doc/reference/index.html". Note that generated documentation files are not
under version control and hence not contained in the repository. As mentioned
above, it is therefore recommended to download one of the packaged release
files in order to have ready-to-use documentation.
Code Quality
------------
For the C++ parts of EMB², we respect most rules of the "Google C++ Style
Guide" which are checked using the cpplint tool. However, we ignore some
rules, as they are not applicable or yield false results for this project.
For example, we respect the include order of the Google Style Guide, but use
<> instead of "" for project includes, which confuses the cpplint tool.
Moreover, we do not tolerate compiler warnings and regularly check the source
code using Cppcheck, a static analysis tool for C++.
Known Bugs and Limitations
--------------------------
- For memory management reasons, the number of threads EMB² can deal with
is bounded by a predefined but modifiable constant (see functions
embb_thread_get_max_count() / embb_thread_set_max_count() and class
embb::base::Thread).
- While MTAPI fully supports heterogeneous systems, the algorithms and
dataflow components are currently limited to homogeneous systems.
Important Notes
---------------
- The MTAPI C++ interface supports automatic initialization, which allows for
easy usage of the MTAPI C++, Algorithms, and Dataflow components. For
performance measurements, explicit initialization is strongly recommended
since the measurements will otherwise include the initialization time of
MTAPI.
- When using ThreadSanitizer there is a bug that causes the built-in CMake type
size determination to fail which in turn leads to a broken configuration.
Therefore, you have to do a normal build first and then rerun CMake with
flags and libs configured for ThreadSanitizer.
Components
----------
EMB² consists of various components. For some of them, there exist C and C++ versions, others are only implemented in C++. The directory names are postfixed with either "_cpp" or "_c" for the C++ and C versions, respectively. Currently, EMB² is composed of the following components:
- Base library: base_c, base_cpp
- MTAPI: mtapi_c, mtapi_cpp, and mtapi_plugins_c (mtapi_network_c, mtapi_opencl_c, mtapi_cuda_c)
- Algorithms: algorithms_cpp
- Dataflow: dataflow_cpp
- Containers: containers_cpp
Directory base_c contains abstractions for threading, synchronization, atomic operations, and other functionalities. As the name indicates, the code is implemented in C. Directory base_cpp contains C++ wrappers around the base_c functions. Similarly, the MTAPI task scheduler is available for programs written in C (mtapi_c) or C++ (mtapi_cpp). Heterogeneous and distributed systems are supported via the plugins contained in mtapi_plugins_c. Directory algorithms_cpp provides high-level constructs for typical parallelization tasks in C++, and dataflow_cpp generic skeletons for the development of parallel stream-based applications. Finally, containers_cpp provides data structures for storing objects in a thread-safe way.
 ### Community and Contact
GitHub:
- https://github.com/siemens/embb
Repository:
- https://github.com/siemens/embb.git (HTTP)
- git@github.com:siemens/embb.git (SSH)
Mailing lists:
- embb-announcements@googlegroups.com (announcements)
### Community and Contact
GitHub:
- https://github.com/siemens/embb
Repository:
- https://github.com/siemens/embb.git (HTTP)
- git@github.com:siemens/embb.git (SSH)
Mailing lists:
- embb-announcements@googlegroups.com (announcements)